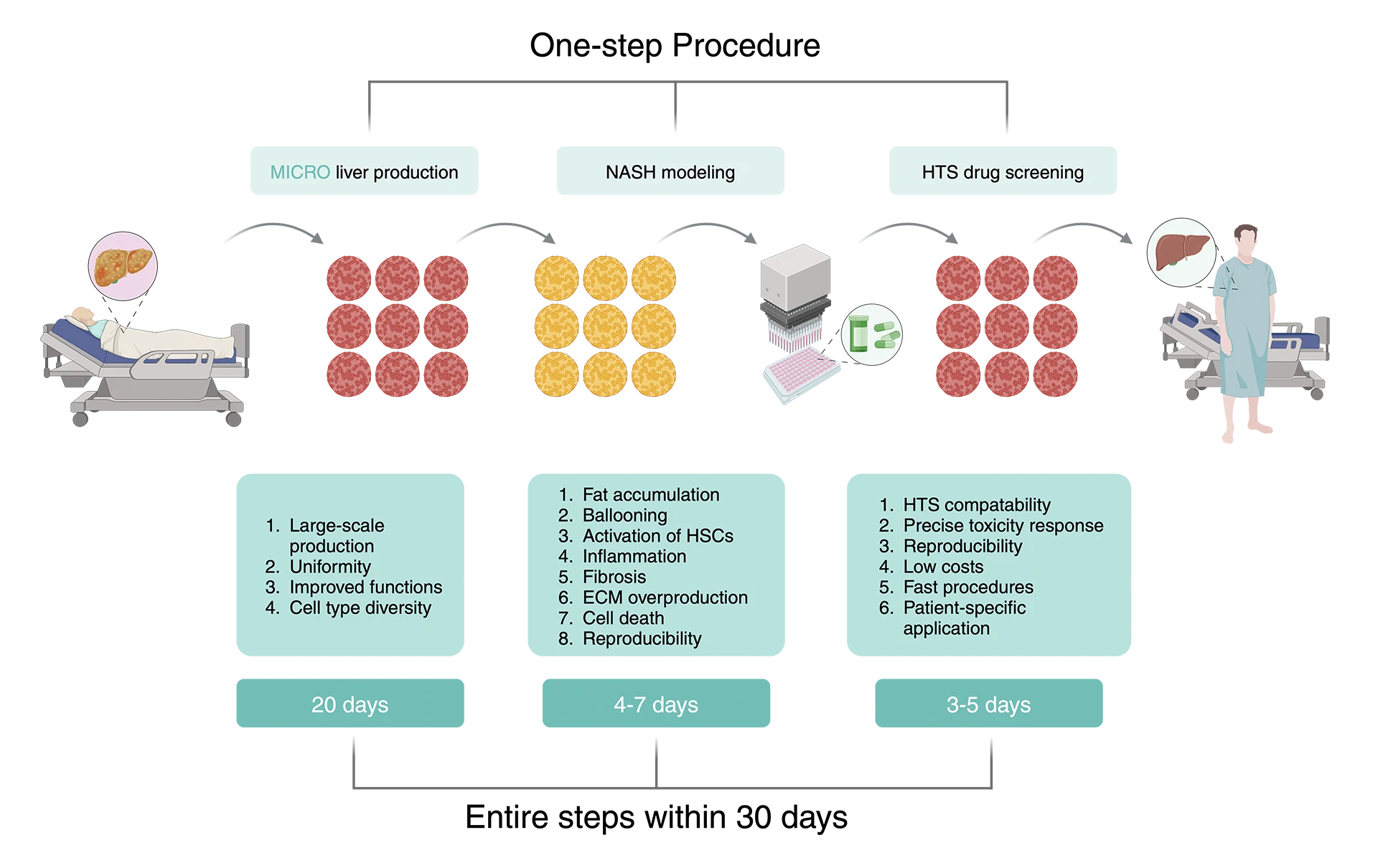
The number of liver disease patients is increasing rapidly both domestically and internationally, and liver organoids are considered an advanced platform for in vitro disease modeling and drug screening. At present, liver organoids are mainly composed of parenchymal cells (liver cells and bile duct cells), lacking non parenchymal cells (such as pro fibrotic/immune cells), thus limiting their ability to simulate liver diseases. NUOXINTE Biotechnology is committed to providing high-quality liver organoids MICRO Liver® derived from human induced stem cells (hiPSC) using optimized unique differentiation techniques 。 Mass production of MICRO Liver® using high-throughput platforms Containing multiple types of cells, both parenchymal and non parenchymal, with mature functions, it can simulate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and exhibit pathological features of the disease. NUOXINTE Biotechnology Micro liver® It can be used as an in vitro high-throughput drug toxicity detection, in vitro modeling of human liver diseases, and a screening platform for therapeutic drugs.
MICRO Liver®, a novel platform for producing large-scale uniform liver organoids
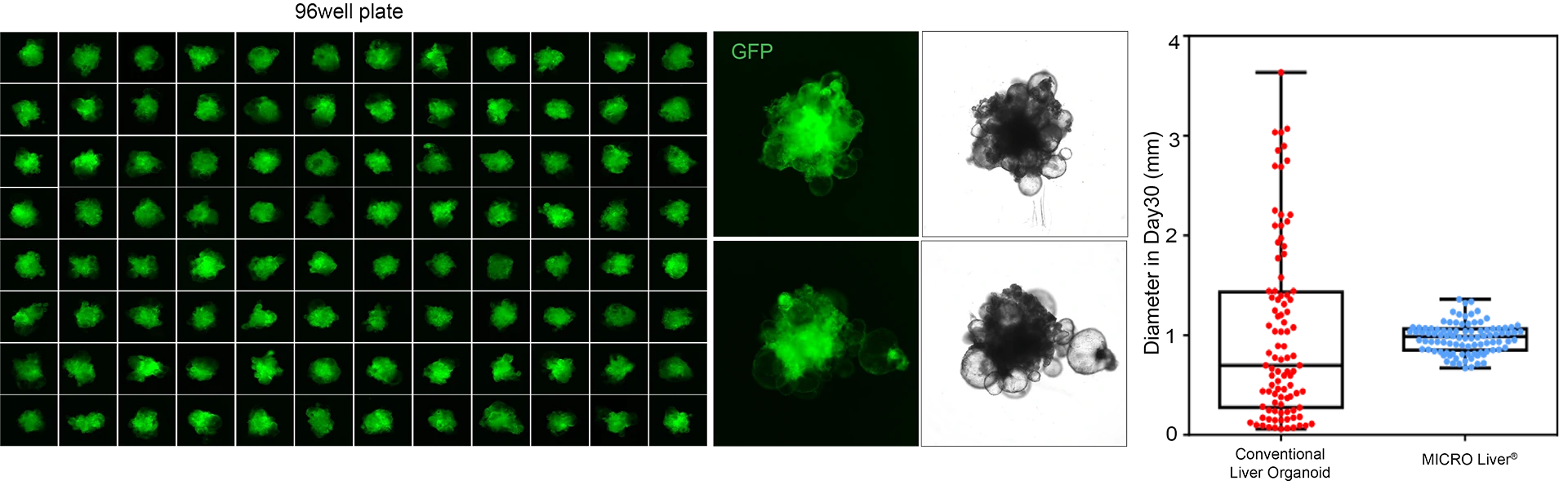
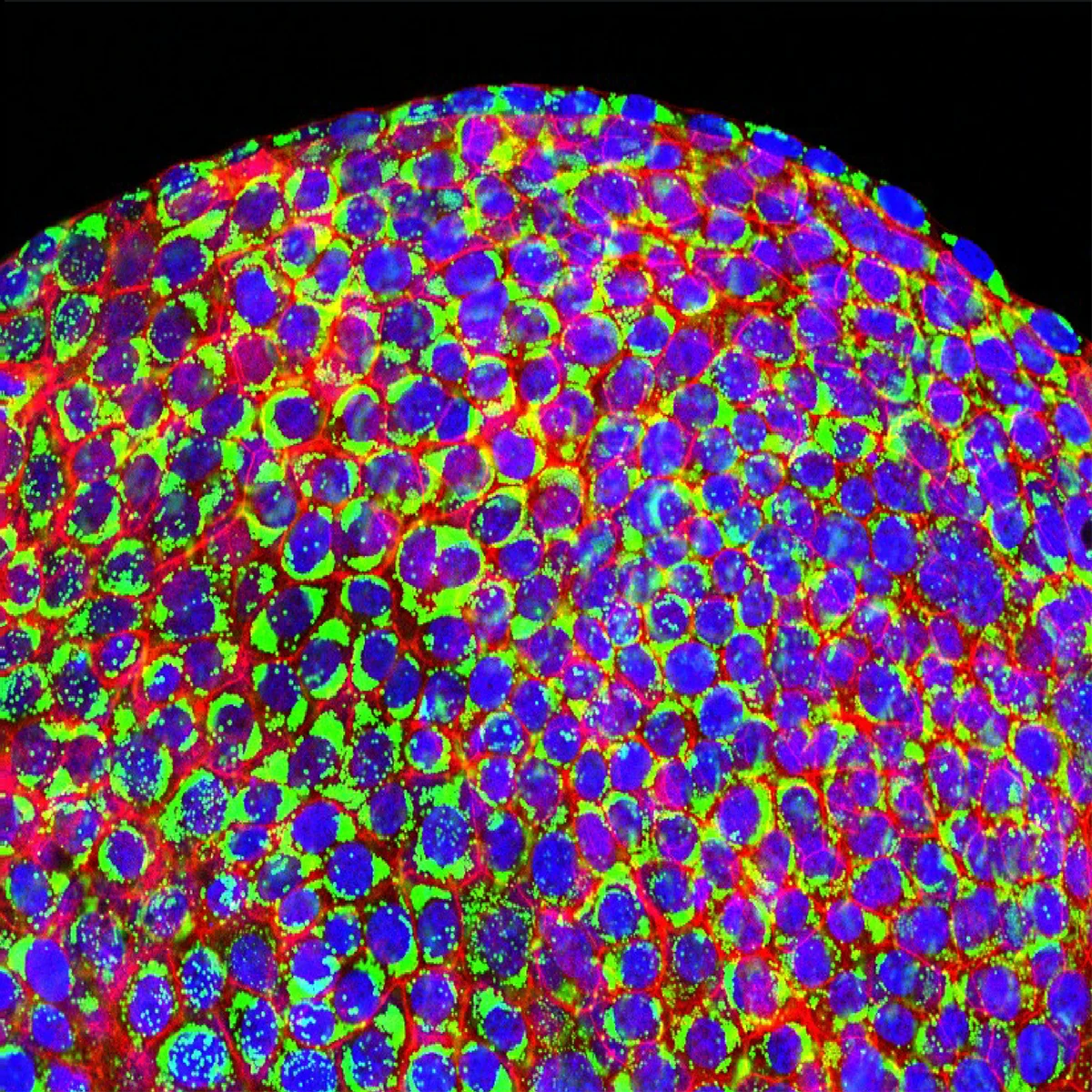
MICRO Liver® generated in 96 well plate (Left). MICRO Liver® exhibits a solid liver cell in the middle, surrounded by cystic bile duct morphology (middle). Compared to traditional liver organoids, MICRO Liver® exhibits smaller individual differences (right).
MICRO Liver®, similar to cell types in the body
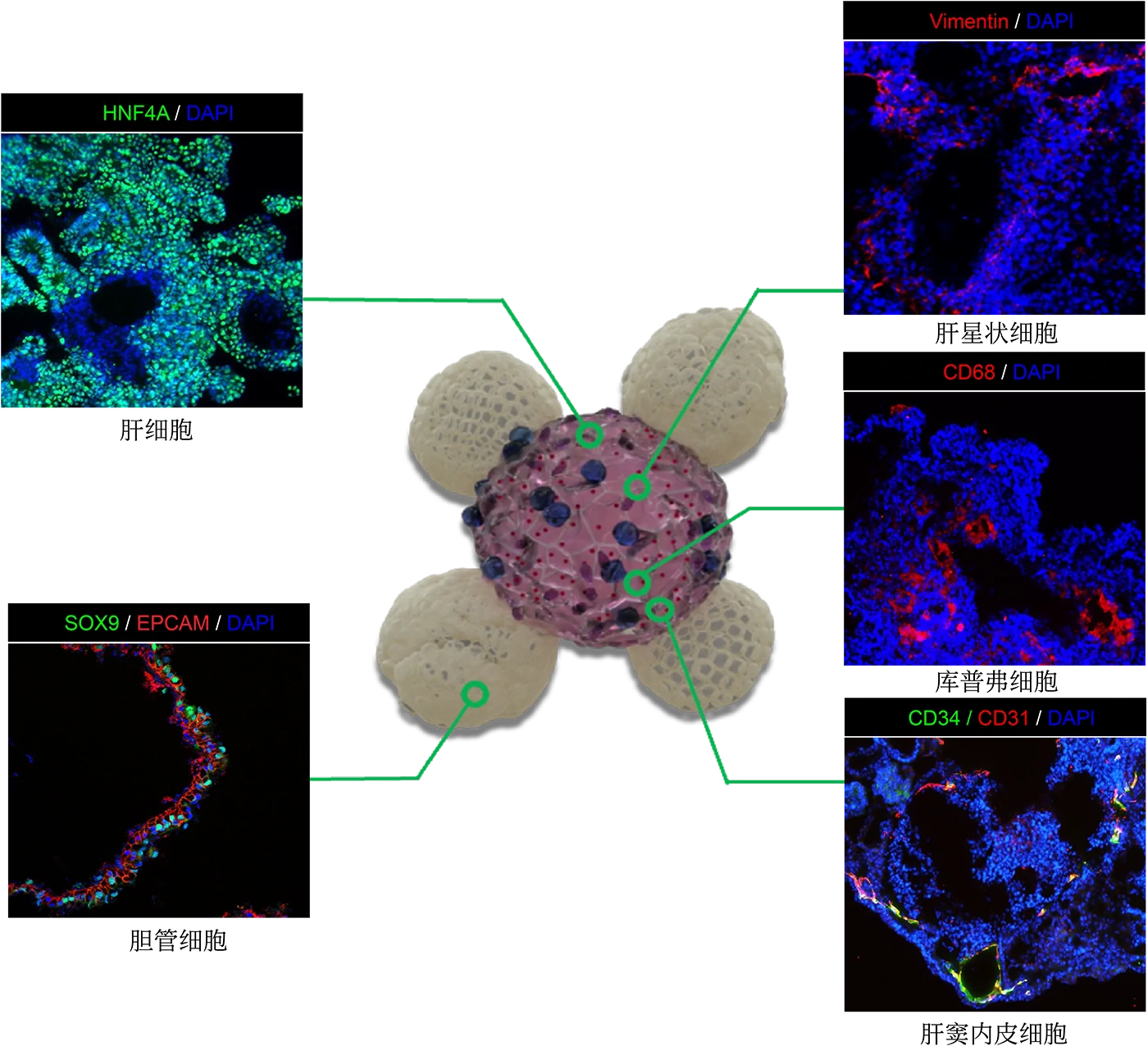
MICRO Liver® is composed of multiple cell types, including hepatocytes (HNF4A), bile duct cells (SOX9, EPCAM), hepatic stellate cells (Vimentin), Kupffer cells (CD68), and sinusoidal endothelial cells (CD34, CD31).
MICRO Liver® exhibits normal liver function
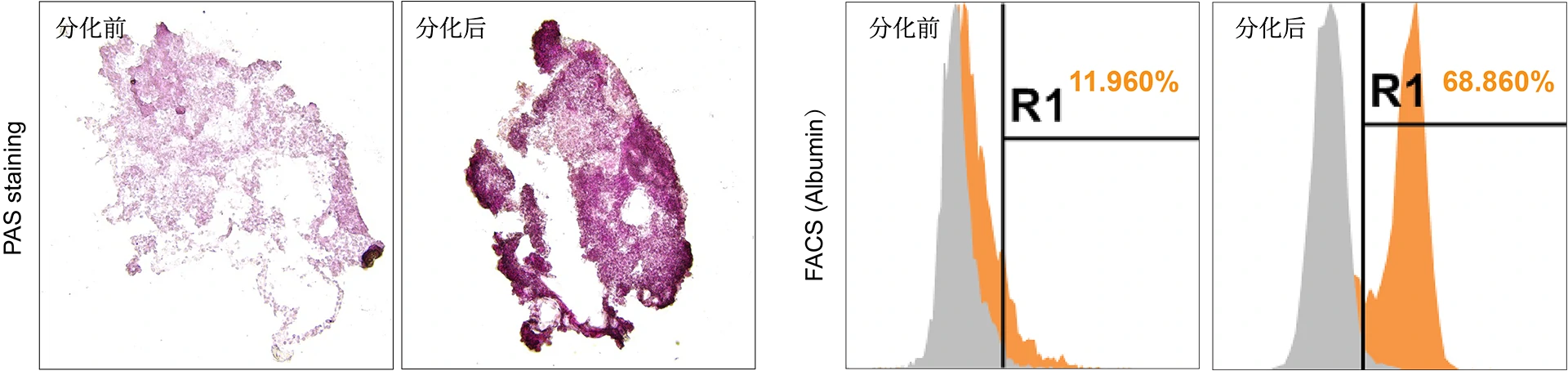
MICRO Liver® exhibits higher functionality after further differentiation. The glycogen storage capacity and albumin positive cells are both increased.
Diversified Applications of MICRO Liver®
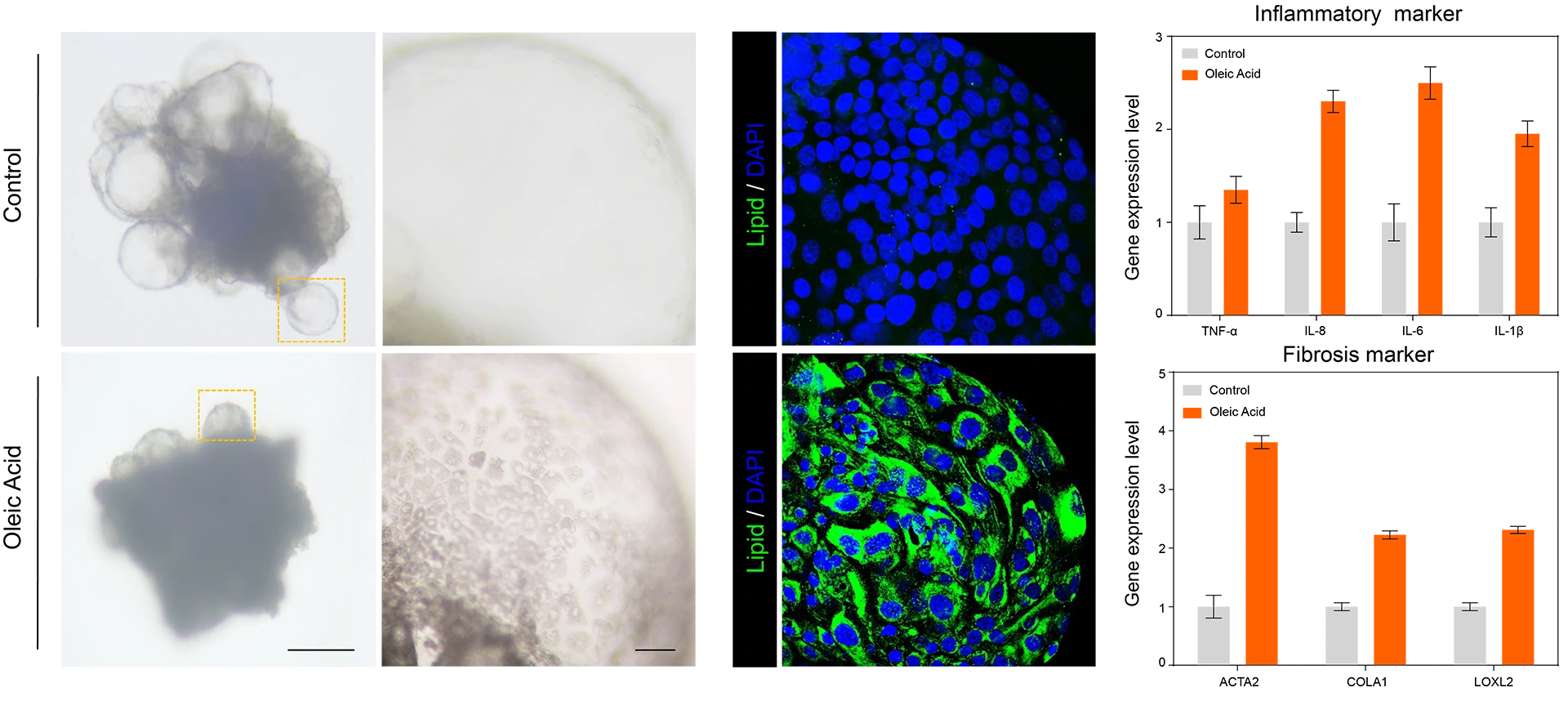
MICRO Liver® uses oleic acid to simulate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD MICRO Liver® observed lipid accumulation (left), as well as an increase in inflammatory and fibrotic factors (right).
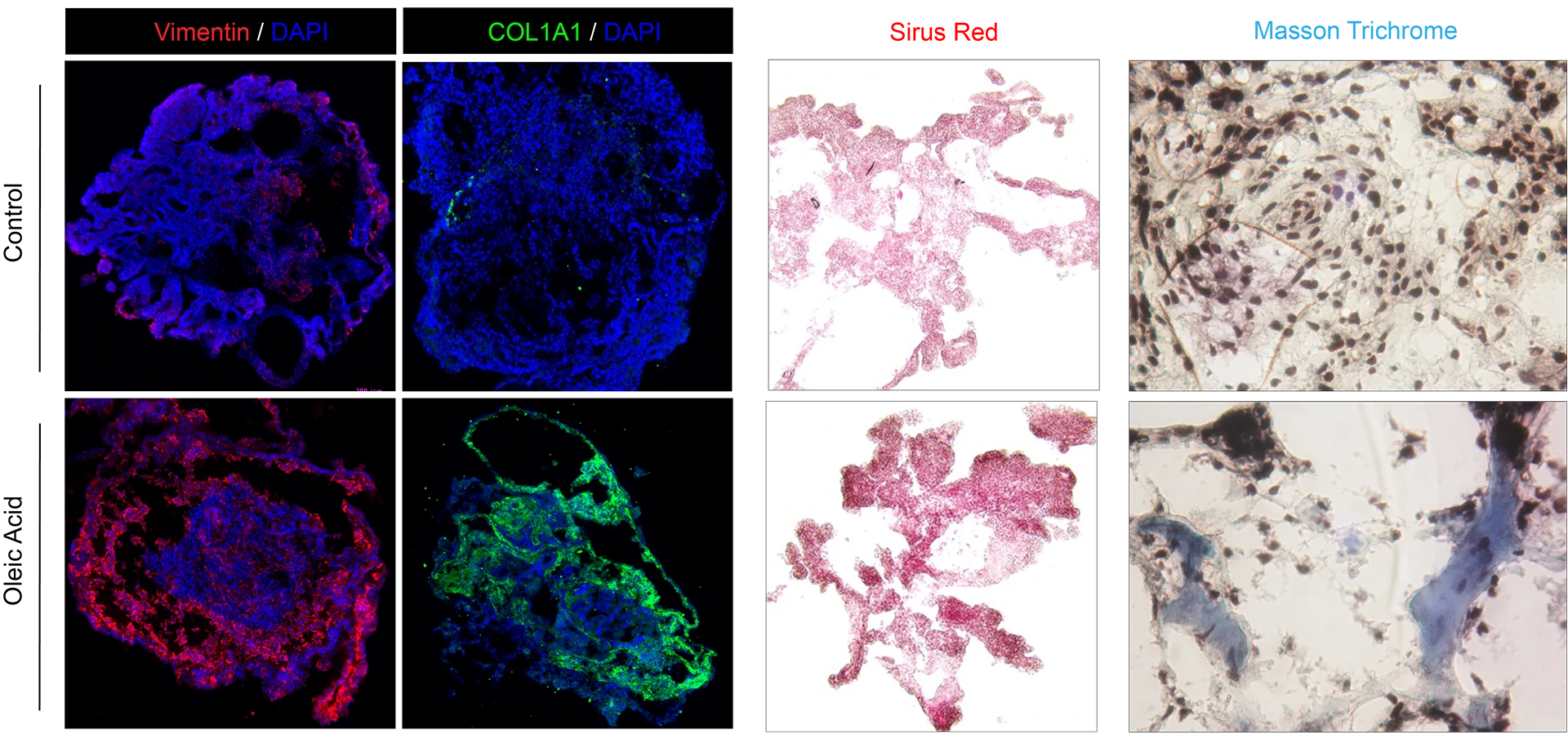
NAFLD MICRO Liver® observed an increase in fibrosis genes (COL1A1, Vimentin) and aggregation of collagen.
One step solution for NAFLD drugs